Editor's Choice
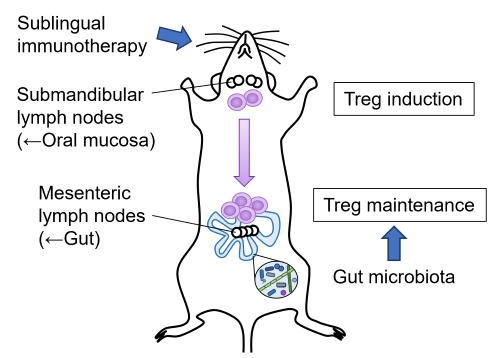
Editor’s comment: Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) induces allergen-specific Treg cells in submandibular lymph nodes, but how these cells are maintained over the long term is unknown.
Winias et al. (Miyagi, Japan) showed that the long-term maintenance of SLIT-induced regulatory T cells critically depends on the gut microbiota. Using a mouse SLIT model, the authors demonstrated that depleting the gut microbiota after SLIT abolishes tolerance and disrupts Treg maintenance. These findings highlight the gut microbiota as an essential driver of durable SLIT-induced immune tolerance.
Editor’s comment: Allergen sensitization patterns are complex, and it is often hard to know which allergens truly matter for each patient.
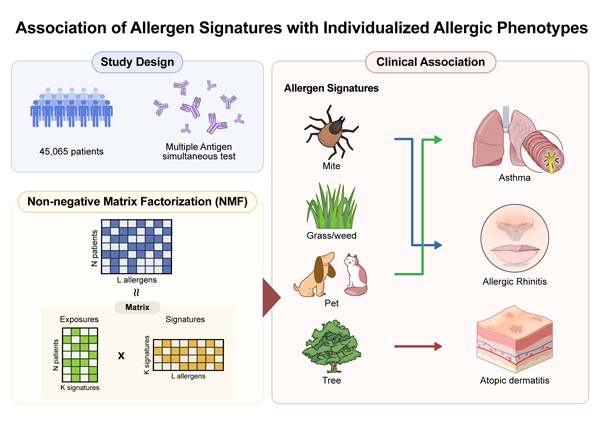
Using IgE test data from over 45,000 people, Kim et al. (Seoul, South Korea) identified four main allergen patterns: mite, grass/weed, pet, and tree. Each pattern showed a different link to disease—mites to hay fever, pets to asthma, and trees to eczema—and was also related to higher eosinophils and total IgE.
This data-driven approach helps clarify which allergens drive each person's allergic reactions.
Review Series: Clinical Remission in Asthma and Related Diseases: Current Landscape and Future Perspectives
Therapeutic approaches that aim for clinical remission—and efforts to overcome the barriers that impede its achievement—have the potential to elevate care for patients with asthma and EGPA. Such strategies may not only improve day-to-day disease control but also enhance long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction. It is our hope that this review series provides a foundation for future research and contributes to the advancement of remission-centered, patient-focused management in asthma and related diseases.
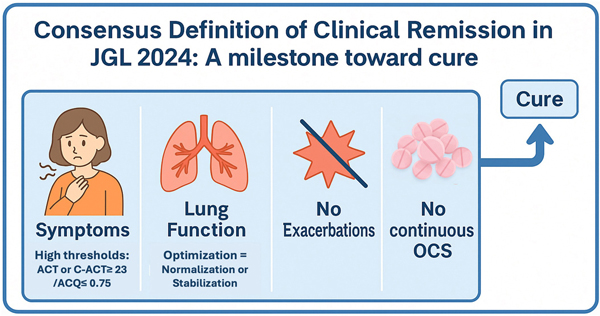
Nagase et al. summarizes the consensus definition of clinical remission adopted in the 2024 Japanese Asthma Prevention and Management Guidelines (JGL 2024).2 Through a two-round modified Delphi process, experts agreed on four core components: absence of exacerbations, well-controlled symptoms, no continuous oral corticosteroid use, and optimization of lung function—defined as normal when achievable and stable when fixed airflow limitation is present.
Hamada et al. focuses on severe asthma, where biologics targeting IL-5, IL-4/13, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and IgE have transformed disease control.3 Across trials and real-world studies, approximately one-third of patients achieve clinical remission, although prevalence varies with definitions and baseline characteristics.
Tamaki revisits remission in EGPA, traditionally defined by BVAS-based inactivity of vasculitis.4 Emerging evidence highlights the inadequacy of classifying patients as "in remission" while they remain dependent on glucocorticoids, even at low doses. Recent biologic trials now include stringent steroid thresholds (e.g., prednisone ≤4 mg/day) within primary endpoints, reflecting a shift toward minimizing glucocorticoid toxicity as a core dimension of remission.