Volume 70, Issue 1 (January 2021)
Editor's Choices
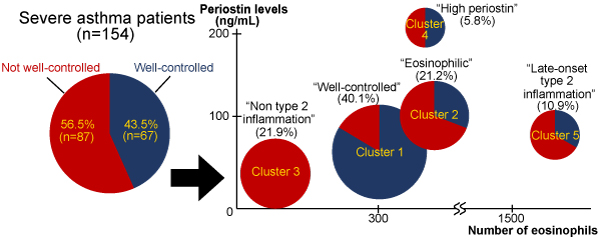
Editor’s comment: Accumulating evidence indicates that an accurate assessment of asthma phenotypes provides information vital for predicting future risk and for directing asthma management. Tanosaki et al. performed a cluster analysis of patients with severe asthma who were enrolled at the Keio Severe Asthma Research Program, revealing that the patients could be divided into five clusters. The authors also showed that cluster 3 (Non-type 2 inflammation), characterized by low eosinophil counts, low periostin levels, and less frequent olfactory disturbance, had the worst asthma control.
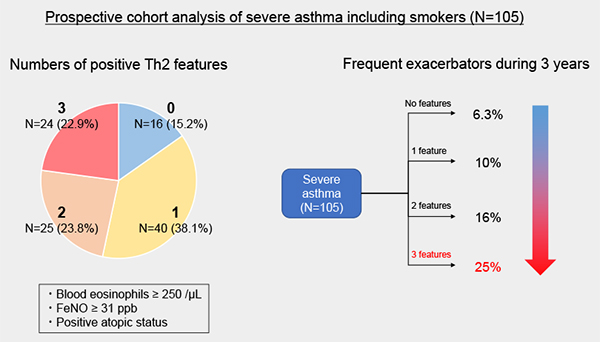
Editor’s comment: It has been reported that severe asthma patients with frequent exacerbations had eosinophilia and higher levels of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) compared with non-exacerbators. Kimura et al. attempted to determine the exact cutoff values of blood eosinophil counts and FeNO related to exacerbation in 105 severe asthma patients in the Hokkaido Severe Asthma Cohort Study. To do so, they used receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. They found that the cutoff values for positive Th2 features were 250 cells/mL in blood eosinophil counts and 31 ppb in FeNO. The values of these positive Th2 features were significantly associated with exacerbation frequencies over three years.
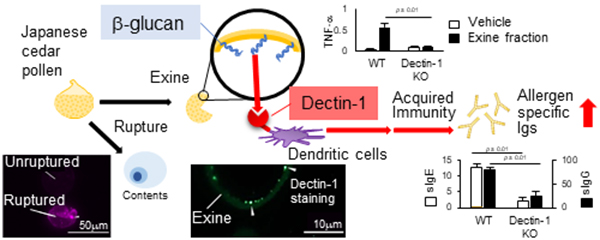
Editor’s comment: The pollen grains of several plant species contain 1,3-β-D-glucan (BG), which activates dendritic cells (DCs) and regulates innate immune responses. Kanno et al. examined the immunological effects of BG in Japanese cedar pollinosis (JCP). BG, found in the JCP pollen grains, stimulated TNF-α and IL-6 production in DCs via a Dectin-1-dependent mechanism. Dectin-1–deficient mice exhibited lower JCP-specific IgE levels than wild-type mice, suggesting that latent BG in JCP can act as an adjuvant to induce JCP-specific IgE production.
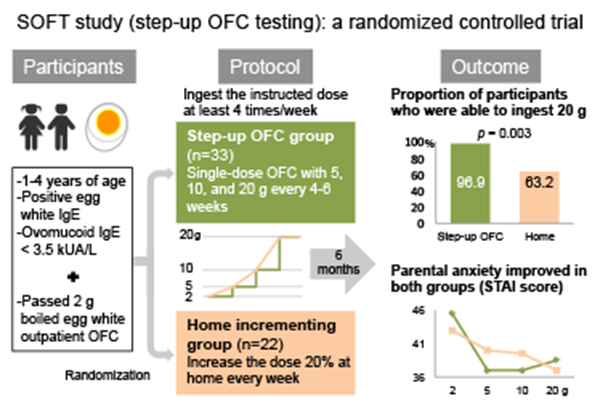
Editor’s comment: Hen's egg is one of the most common food allergens in childhood food allergies. However, little is known about parental anxiety arising during and after dietary instruction for children with suspected egg allergy. Kitamura et al. compared the efficacy, safety, and parental anxiety related to two different dietary instruction methods (the step-up oral food challenge testing (SOFT) method or the home incrementing method) of introducing boiled egg white. They found that the SOFT method of dietary instruction was more effective than the home incrementing method for children with suspected egg allergy. Meanwhile, no serious adverse reactions were observed in either group.