Volume 71, Issue 3 (July 2022)
Editor's Choices
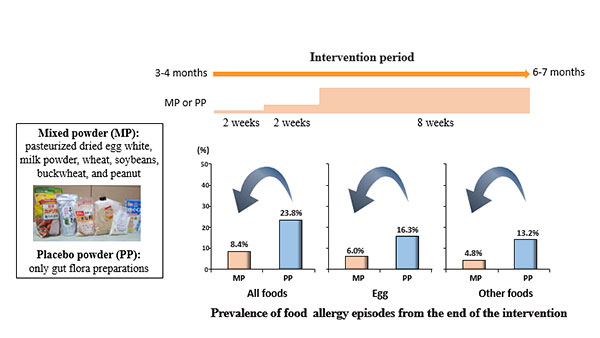
Editor’s comment: Several trials have suggested a possible protective role of the early introduction of allergenic foods against food allergies. In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Nishimura et al. investigated whether multiple food allergies in infants 3-4 months old with atopic dermatitis could be safely prevented by simultaneously administering small amounts of multiple foods, using mixed allergenic food powder containing egg, milk, wheat, soybean, buckwheat, and peanuts. They found that gradually increasing the intake of small amounts of multiple foods in early infancy can safely reduce the incidence of egg allergies.
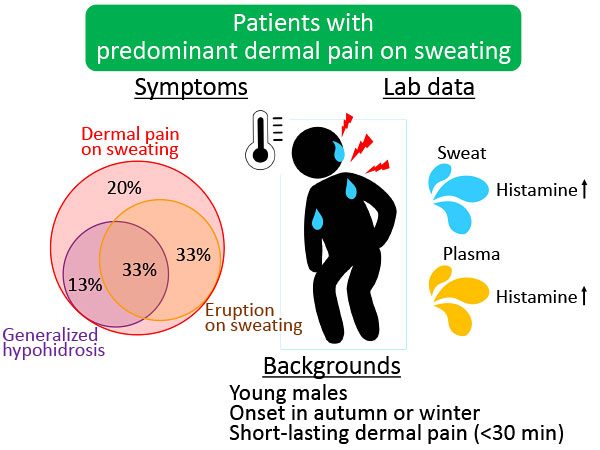
Editor’s comment: Some patients with cholinergic urticaria (CholU) suffer from uncomfortable tingling pain rather than from pruritus. Patients with acquired idiopathic generalized anhidrosis (AIGA) are also often troubled by tingling dermal pain upon sweating. To obtain insight into the underlying mechanism, Takahagi et al. retrospectively analyzed clinical and histopathological characteristics of patients who predominantly presented with tingling dermal pain triggered by sweating. They found that sweat histamine and increased plasma histamine after thermal induction were significantly higher than those in healthy subjects, suggesting the involvement of sweat and plasma histamine in tingling dermal pain.
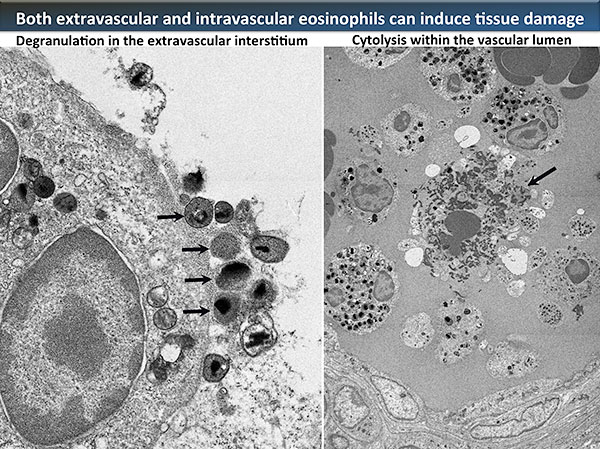
Editor’s comment: Although eosinophilic inflammation is a characteristic feature of involved tissues in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), the mechanism underlying tissue damage remains largely unknown. In this study, Koike et al. used electron microscopy to examine the morphological bases underlying eosinophil-associated lesions in sural nerve biopsy specimens in patients with EGPA. They found that most eosinophils in both the vascular lumen and extravascular interstitium showed morphological changes suggestive of piecemeal degranulation, irrespective of the ANCA status, suggesting that degranulation is inducing the tissue damage.