Volume 74, Issue 3 (July 2025)
Editor's Choice
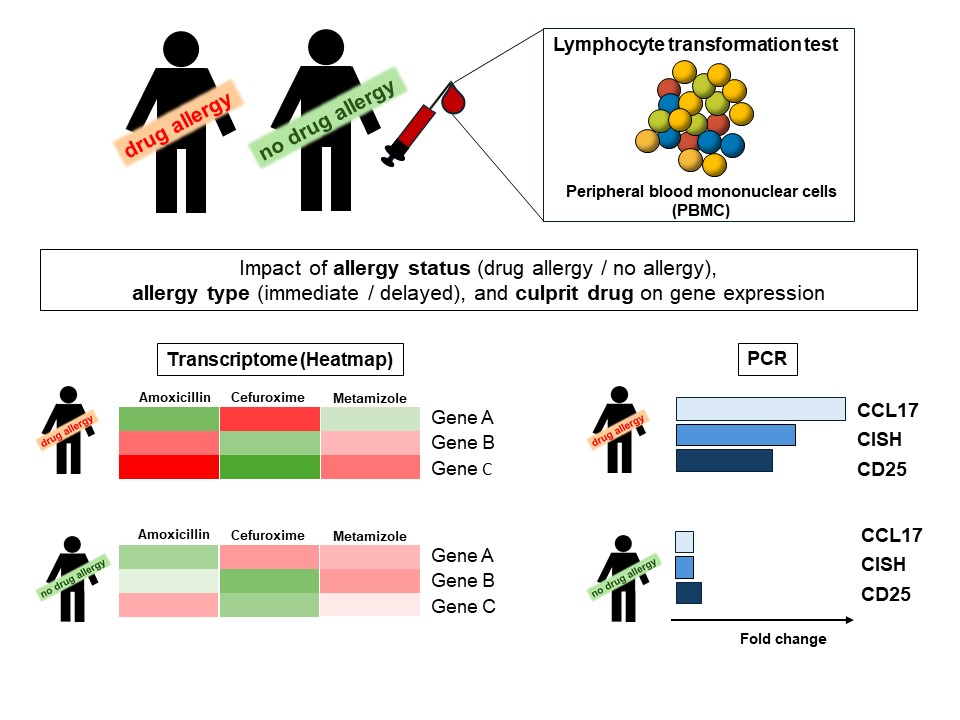
Editor’s comment: The lymphocyte transformation test (LTT) is used for the in vitro detection of drug sensitization in patients with an assumed drug allergy. In the LTT, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from the patient and a non-drug allergic control person are incubated in vitro with the culprit drug, followed by evaluation of T cell proliferation or Th1/Th2 cytokine expression. However, these read-out methods present with varying sensitivity depending on parameters such as the allergy type (immediate or delayed), the allergy-inducing drug, or the time to testing. Glässner et al. present a new idea, to use a genome-wide gene expression analysis ("transcriptomics") to identify the culprit drug after in vitro stimulation of PBMC from drug-allergic patients. The authors' findings may lead to the identification of one or a panel of genes associated with specific drug allergies and could provide the basis for a reliable in vitro method to detect drug sensitization in patients.
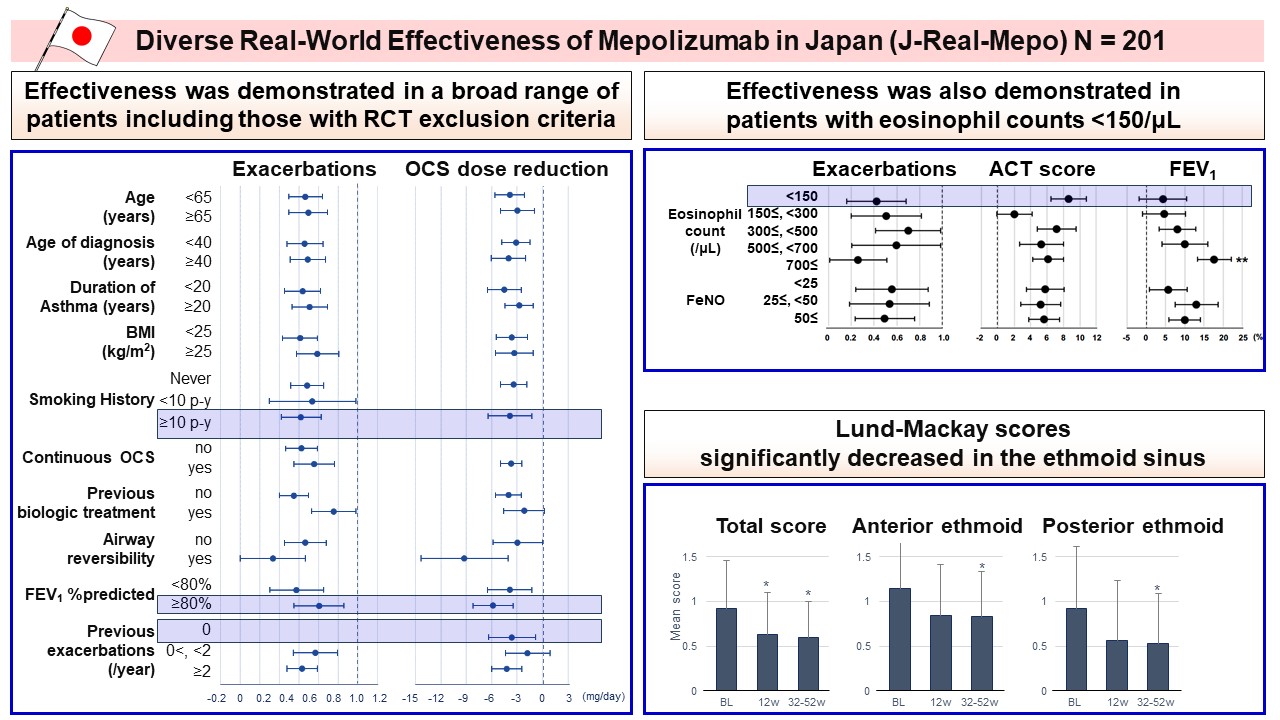
Editor’s comment: Although randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the efficacy of anti-IL-5 antibody Mepolizumab on asthma, they have excluded certain patient subgroups. To bridge the gap between RCTs and real-world practice, Nagase et al. conducted a retrospective observational study in Japan (J-Real-Mepo: UMIN000045021) and evaluated the effectiveness of Mepolizumab in a diverse population, including those potentially excluded from RCTs. The authors found that Mepolizumab showed effectiveness in a broad range of patients, including those with RCT exclusion criteria who had a significant disease oral corticosteroid (OCS) burden.